1.翻译的基本步骤
专业英语的翻译应遵循以下四个步骤。
(1)阅读理解。先大致浏览一遍全文,了解专业背景,理解大意。这里所说的理解不同于一般的阅读理解,而是要为翻译作准备,任何一点都不能似是而非。
(2)翻译准备。查字典掌握生词的含义,对于专业词汇最好是查专业词典。
(3)汉语表达。用汉语将原作表达出来,力求忠实于原作、通顺流畅。当原作与汉语的表达方式存在较大差异时,可对原作适当进行一些增删或延伸。
(4)检查校对。在翻译初稿完成之后,要仔细校对原文,尤其要注意一些与汉语表达方式不一致的数据和图表等,以免造成谬误。翻译的核心工作就是汉语的表达,在这过程中,要综合运用各种方法和技巧。
2.直译
直译即照英文直接翻译,它包括两个方面的内容:一是基本上保持原文的语法结构,即在语序和词序上不做较大的变动;二是保留原文词语的字面意义。对于专业英语来说,在能保证译文“信”“达”的情况下,应尽量采用直译。
[例1]The passengers shall stand at the right side of the auto staircase and leave the left side open for traffic.
乘客应该站在自动扶梯的右边,左侧留出来以便通行。
[例2]The new type of train is called maglev.
这种新型火车被叫作磁悬浮列车。
这两句译文是典型的直译。因为英语与汉语在语序和词序上存在着较大差异,所以像这样直译的情况并不多。语序和词序稍作变动的情况则是很常见的。
[例3]The development of energy accumulator used for urban rail transit system.
城市轨道交通系统储能器的发展。
[例4]Application of D-type power amplifier in ATP system digital track circuits of urban transit.
D类功率放大器在城市轨道交通ATP系统数字轨道电路中的应用。
3.转换
专业英语虽然不像文学英语那样在翻译上有较大的自由度,但要想使译文能符合汉语的语法和修辞习惯,在很多情况下都需要做一些“修饰”,如语序的重大调整、句子成分的改变、句子结构和句子表达方式的转换、词义的引申等。
(1)词义的转换。翻译时,如果词典中没有合适的词义来表达某个词汇,可对其意义加以引申,但不能改变原意。
[例]If the computer control system fails,the backup system automatically takes up the failed system,and there is no working pause.
如果该计算机控制系统发生故障,其备份系统自动接替故障系统继续工作,从而不致产生工作停顿。
(2)词性的转换。所谓词性的转换是将英语中某一类词性的词转换成汉语中另一类词性的词。可以转换的词类很多,如:名词→形容词、形容词→副词、动词→形容词、副词→名词、副词→形容词、副词→动词等。
[例1]Reliability features this control system.
可靠性是这个控制系统的特色。(动词转换成名词)
[例2]We find difficulty in solving this problem.
我们觉得难以解决这个问题。(名词转换成副词)
[例3]The experiment is over.
试验结束了。(副词转换成动词)
(3)句子成分的转换。当英语和汉语的语法习惯发生冲突时,可以将原文句子中的某一语法成分(主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语和状语等)改译成另一种语法成分。这样的转换非常灵活,具体如何转换要视具体情况而定。
[例1]Attempts were made to find out a method for increasing productivity.
(我们)曾力图寻找一种提高生产率的方法。(主语转谓语)
[例2]The results are in good agreement with those obtained by theoretical deduction.
此结果与理论推导所得到的结果完全一致。(表语转换成谓语)
(4)句子结构的转换。句子结构的转换包括将英语的简单句改译成汉语的复合句,将英语的复合句改译成英语的简单句或将一种从句改成另一种从句。
[例1]Computer is known to be one of the greatest inventions.
人们知道,计算机是最伟大的发明之一。(简单句转换成复合句)
[例2]The signal showed that the device was in order.
信号表明,设备一切正常。(简单句转换成复合句)
[例3]What a motor does is to change electrical energy into mechanical energy.
电动机的作用就是把电能转换成机械能。(主语从句换成简单句)
[例4]Click the bitmap button,a dialog box will pop up.
如果点击位图按钮,就会出现一个对话框。(并列句换成条件从句)
(5)表达方式的转换。专业英语的被动语态很多,有时候为了使译文更顺畅,可将英语的被动语态译成汉语的主动语态。此外,英语中的肯定(否定)语气也可以转换成汉语的否定(肯定)语气。
[例1]Any cipher can not remain indecipherable for long.
任何密码都不能长期不被解密。(主动语态转换成被动语态)
[例2]There is no rule that has no exceptions.
凡事均有例外。(否定句转换成肯定句)
4.省略
任何一篇好的译文并不一定是对原文逐字逐句的翻译,而是根据汉语的语法和修辞习惯,省略掉一些原文中的词语,如冠词、代词和关联词等。这些词或者是没有实意,或者是没有必要翻译。
(1)省略冠词。
[例]The memory is an important part of a computer system.
存储器是计算机系统中的重要组成部分。
(2)省略代词。
[例]If you know the frequency,you can find the wave length.
如果知道频率,就可求出波长。
(3)省略关联词。
[例]This new type of microcomputer is so small that one can hold it in hand.
这种新型微机如此小以致一个人可以将其拿在手中。
(4)省略没有必要的翻译。
[例]The flow chart shown in Fig.1 is intended to illustrate the programming process.
图1为表明程序设计过程的流程图。
5.增补
有省略,自然也就有增补。主要是用在采用以上方法翻译的译文不能完全符合汉语的语法和修辞习惯的情况下,但增补不能过多,更不能加入一些译者本人的思想和观点。要忠实于原作。
(1)增补名词。
[例]Reading 读书
Preparation 准备工作
(2)增补动词。
[例1]Networking 联网
[例2]We had a survey meeting after experiment.
试验结束之后,我们举行了鉴定会。
(3)增补量词。
[例]Three computers 三台计算机
A chip 一片芯片
Two months 两个月(但two days和two years并不用加量词)
(4)增补副词。
[例]The speed is fast 速度很快
High price 价格很高
(5)增补表示复数的词。
[例]The first production 第一批产品
The experts 专家们
(6)增补原文省略掉的词。
[例]Three symbols are used to represent the three types of bus,the symbol for data bus is D.B.,for address bus A.B.,for control bus C.B..
我们用三种符号来表示三种总线,用符号D.B.表示数据总线,用符号A.B.表示地址总线,用符号C.B.表示控制总线。
6.词的翻译
这里仅介绍常遇到最多的实词——名词和动词的翻译方法。
(1)普通名词。普通名词的意义很多,在翻译时应根据上下文来选择最恰当的含义,切忌望文生义,主观臆测。一般要注意以下三个方面的问题:①直译和转换;②单复数的区别;③多义词的翻译。关于直译和转换,上述已介绍。对单复数的区别,除了注意要增添量词外,有时候根据需要还要增添数量词,如“一个”“一件”“这些”“若干”和“种种”等。多义词的翻译首先应考虑专业范围的含义,然后再考虑其他领域的含义,拿不准的要查字典或请教有关方面的专家。
[例]Sensors are mounted near the tested objects.
各种传感器都安装在被测对象的附近。
(2)专有名词的翻译。专有名词包括:人名、公司及社团名、商品或产品名、商标名、型号及标准号和地名等。一般的原则是:名从主人,约定俗成,直接音译。
[例1]England按英语译成“英格兰”,Germany按德语(Deutsch)译成“德意志”。
[例2]一些人名、地名、数量单位和专业术语已经是使用多年的,如:瓦特、爱因斯坦等,不必再标新立异。
(3)缩写词和符号的翻译。缩写词大多是首字母,可按意义直译,而对于大家都很熟悉的公司、机构或专业术语的缩写词也可不译,照抄原文。至于单位则按意义直译或不译直接引用。
[例1]IBM 照抄或译成:国际商业机器公司(International Business Machines corporation)
ATC 列车自动控制系统(Automatic Train Control)
ATP 列车自动保护系列(Automatic Train Protection)
FAS 防灾报警系统(Fire Alarm System)
[例2]rpm 转/分(round per minute)
km/h 千米/小时(kilometer per hour)
dpi 点/英寸(dot per inch)
bps 位/秒(bit per second)
(4)动词的翻译。动词的翻译与句子的译法一样,也有直译、转换、增补和省略等方法。
[例1]A digital computer comprises five basic units:input,output,memory,control unit and arithmetic-logic unit.
数字计算机由五个基本部件组成:输入、输出、存储器、控制部件和算术逻辑部件。(直译)
[例2]An electric current varies directly as the electromotive force and inversely as the resistance.
电流的变化与电动势的变化成正比,与电阻成反比。(词性转换)
[例3]Nyquist's open-loop gain frequency-response form of solution of the feedback stability problem was of immense practical value.
利用奈奎斯特开环增益频率响应曲线来解反馈系统稳定性问题具有极大的实用价值。(转换和增补)
[例4]We must make the phenomena clear.
我们必须把这个现象弄清楚。(词性转换)
7.句子的翻译
句子的翻译除了要遵循一般的规律之外,对特别的句子结构还应该掌握一些特殊的方法,如顺译、倒译、转换、增删等。以下举例简要介绍复合句、否定句和长句的翻译方法。
(1)复合句的翻译。
[例1]That Java is the next century programming language is accepted by most of us.
Java是下个世纪的编程语言的说法被我们大多数人接受。(顺译,即按原文顺序译成主语从句)
[例2]It is no matter that we design the control system using microcomputer or single chip micro-processor.
我们用微型计算机还是单片机来设计该控制系统都无关紧要。(倒译,从句译作主语,主句中的谓语部分译作谓语)
[例3]There is another reason why A.C.is preferred to D.C.for long-distance transmission.
为什么长途输电时交流电优于直流电,还有另外一个原因。(定语从句转换成主语从句)
复合句分并列复合句和主从复合句。由and、or、but等连词连接的并列复合句,通常都采用顺译的方法;而由for、therefore等连词连接的并列复合句通常都译成主从复合句。
[例4]Modern personal computer is smaller and smaller,but it has more and more functions.
现代的个人计算机越来越小,但功能却越来越多。(顺译)
[例5]In the near future,almost all of our families are equipped with telephones and therefore we can link our PCs together by dial networking.
不久的将来,几乎所有的家庭都安装上电话,因此我们可以通过拨号上网的方式把我们的PC机连接起来。
主从复合句有两类,一类是由关联词with和从属连词that等引导的复合从句;另一类是由引导词it引导的主语从句。翻译中可采用的方法很多,限于篇幅仅举一例略作说明。
[例6]The great value of this new material lines in the fact that it can be used in hightech field.
这种新材料的巨大价值在于它能够用于高科技领域。(同位语从句转换成宾语从句)
(2)否定句的翻译。否定句分三种情况:全部否定、部分否定和双重否定。全部否定常用的词有:not,never,not…nor等。部分否定常用的词有:not many,not much,not every,not both,not some等。双重否定常常用not,no,never,neither,nobody,nothing等与其他具有否定意义的词搭配使用。
尤其要注意的是英语中有些词本身并非not,no,un-,dis-等,但也有否定的意义,甚至是很强的否定意义。例如:few,too…(to),but for,instead of,rather than等。
[例1]Without electricity,a computer can not work.
没有电,计算机就不能工作。(全部否定)
[例2]None of the answers are right.
所有的答案都不对。(否定名词)
[例3]Not all of these results are satisfactory.
并非所有的结果都令人满意。(部分否定)
[例4]There is no rule that has no exceptions.(https://www.xing528.com)
凡规则均有例外。(双重否定)
(3)长句的翻译。在句子结构上,通常多采用顺译法,有时为了符合汉语的表达习惯,也可采用倒译法。另外,为了汉语的行文方便,通常都将英文长句拆开,分成若干个短句分别译出。在必要的情况下,译文中可适当增补一些词汇。
[例]For example,the largest early computer occupied a volume of hundreds of cubic meters and required many tens of kilowatts of electrical power and a sizable air conditioning installation to allow this amount of energy to be dissipated without raising the room temperature to unbearable values.
例如,早期最大的计算机要占据数百立方米的空间、需要几十千瓦的电源和一个相当大的空调设备来消除这些设备产生的大量的热,而不至于使室温上升到无法忍受的程度。
(4)标题的翻译。标题的翻译与正文不同,有它的特殊性。一般标题大多采用短语结构,较少采用完整的句子。比较规范化的论文或著作的标题长度应该在一定的字数以下,而且采用简洁、明确的主从短语,因此在翻译时也尽量使用主从语句,特殊情况下,也可作一些变通。如直译原文长句,或加一个小标题等。
[例1]Distributed shared memory algorithms
分布式共享存储器算法
[例2]Performance analysis of a new network access floe control method in computer communication networks
计算机通信网中一种新型网络访问流控制方法的性能分析
[例3]Least-square identification of closed-loop systems
闭环系统的最小方差辨识
8.专业术语的翻译
(1)意译。所谓意译,就是按照英语的意义,从汉语中找出对应的词汇将原文翻译出来。这种方法是专业术语翻译中使用最多的一种方法。为了简化起见,英语中经常使用缩写,汉语也一样,也经常使用缩写。意译的特点是顾名思义。
[例]One way ticket 单程票
Money-inside ticket of“One card through city” 一卡通储值票
Ticket office/Information desk 售票/问询处
Central corridor 客车中间走廊
Peak hours 高峰时间
Off-Peak hours 非高峰时间
Alternating current 交流电
Direct current 直流电
(2)音译。有些专业术语由于种种原因,采用音译。如原文的意义很长、汉语中无对应词汇,只是一种单位、历史沿袭或受港澳台地区的影响等。
[例]radar 雷达
logic 逻辑
hertz 赫兹
clatter 咔嗒声
laser 镭射(激光)
(3)象译。所谓象译即按照所描绘事物的形状来翻译。如果汉语中有相应的说法,则按汉语习惯表达,否则可按英文翻译。
[例]I-cursor I形光标
T-connection T形连接
V-conversion V形转换
T-guideway T状导轨
9.有关数量的翻译
(1)专业英语中常用符号和数学式的表达。
1/2 a half,one haft
1/3 a third,one third
2/3 two thirds
1/4 a quarter,one quarter,a fourth,one fourth
1/100 a hundredth,one hundredth
1/1000 a thousandth,one thousandth
113/324 one hundred and thirteen over three hundred and twenty-fourth
![]() four and two thirds
four and two thirds
0.25 zero point two five
+ plus,positive
- minus,negative
± plus or minus
× multiplied by,times
÷ divided by
= be equal to,equals
≈ be approximately equal to,approximately equals
( ) round brackets,parentheses
[ ] square(angular)brackets
≤ less than or equal to
≥ more than or equal to
∞ infinity
∵ because
∴ therefore
→ maps into
% percent
2% two percent
‰ per mill
5‰ five per mill
∑ the summation of
20° twenty degrees
7′ seven minutes;seven feet
13″ thirteen seconds;thirteen inches
0℃ zero degree Centigrade
100℃ one hundred degrees Centigrade
32°F thirty-two degrees Fahrenheit
(2)数量增减的译法。
①表示增加的译法。
句型
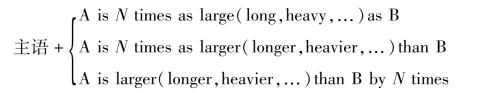
都可以表达一个概念,均可译成:A的大小(长度,重量,……)是B的N倍或A比B大(长,重,……)N-1倍。
[例1]A is four times as large as B.
A为B的四倍或A比B大三倍。(不能译成:A比B大四倍)
[例2]The oxygen atom is 16 times heavier than the hydrogen atom.
氧原子的重量是氢原子的16倍。
[例3]In case of electric scanning the beam width is broader by a factor twice.
电子扫描时,波束宽度展宽一倍。(by a factor twice=by two times)
句型

double可译成:“增加一倍”或“翻一番”
treble可译成:“增加两倍”或“增加到三倍”
quadruple可译成:“增加三倍”或“翻两番”或“增加到四倍”
[例1]Whenever we double the voltage,we double the current.
每当我们把电压增大一倍时,电流就增大一倍。
[例2]The growth rate of GNP(gross national product)per capita for China will be quadrupled by 2000.
到2000年,中国人均国民生产总值的增长率将翻两番。
句型

但有些语法书上对increase by N times有不同说法,一般情况下译成“增加了N倍”,特殊情况下,根据上下文可译成“增加了N-1倍”。
[例1]The production of various ICs has been increased four times as against 1990.
各种集成电路的产量比1990年增长了三倍。
[例2]Since the first transatlantic telephone cable was laid,the annual total of telephone calls between UK and Canada has increased sevenfold.
自从第一条横跨大西洋的电话电缆铺设以来,英国和加拿大之间的年通话量增加了六倍。
②表示减少的译法。
句型

结构的译法:均可译成“减少了(N-1)/N”或“减少到原来的1/N”。上述句型中reduce换成decrease,shorten,drop,step-down,cut down意义相似,均表示“减少”。
由于汉语并不习惯说“减少了多少倍”,而说“减少了几分之几”。所以,翻译时应将N倍换算成(N-1)/N或1/N。如reduce 3 times可换算成:(3-1)/3=2/3,即成“减少了三分之二”或“减少到原来的三分之一”。
[例1]The voltage has dropped five times.电压下降了五分之四。(或电压下降到原来的五分之一)
[例2]The leads of the new condenser are shortened three times as long as those of the old.新式电容器的引线比老式电容器的引线缩短了三分之二。(或新式电容器的引线是老式电容器引线的三分之一)
[例3]Switching time of the new type of transistor is shortened 4 times.新型晶体管的开关时间缩短为原来的四分之一。
此外,还有decrease to,reduce to等,可直译成“减少到”。如:decrease to 50,可译成“减少到50”。
③近似数量的译法。与汉语类似,英语中也有表示近似数量的词。如:over,above,more than,under,below,less than,some,about,nearly,from…to…,between…,and…,more or less等。可译成“上下”“左右”“多于”“少于”“以上”“以下”“大致”等。
另外,还有一些表示一定数量的词组有:
teens of… 十几(13~19)
tens of… 几十
decades of… 几十
dozens of… 几打
scores of… 几十(大于40)
hundreds of… 几百
thousands of… 几千
[例1]over 220 volts 220V以上
[例2]nearly one tenth接近十分之一
[例3]one hundred grams more or less 100g左右
10.长句的译法
(1)顺序译法。英语长句当叙述层次与汉语相同时,可按原文顺序译出。
[例1]The advantages of a maglev(magnetic levitation)transport system are many.A maglev train would be quick,quiet,nonpolluting;the ride would be smooth and comfortable.The tracks could be elevated out of the way of surface traffic.But there are many problems,both technological and financial,that remain to be solved.
磁悬浮交通系统有很多优点。磁悬浮列车快捷、安静、无污染,乘坐起来平稳、舒适,轨道位于地面交通的上方。但是磁悬浮列车也有许多问题,既有技术方面的,也有财政方面的,这些问题仍有待解决。
[例2]Everything on the line has been designed to provide passengers with high quality services.The 7km initial section runs entirely underground,with an end to end journey time of just 11min including 8 stops.This gives a highly attractive commercial speed of 40km/h compared to the 20km/h to 25 km/h achieved on our conventional lines.
这条新线路可以为旅客提供全方位、高质量的服务。第一期线路全长7km,完全处于地下,全程运行时间为11min,有8个停车站。其车速为40km/h,比起常规线路上速度为20~25km/h的列车,它具有很强的商业吸引力。
(2)变序译法。有时英语长句叙述层次与汉语相反,需从英语原文的后面翻译,逆着原文顺序翻译。
[例1]A student of mathematics must become familiar with all the signs and symbols commonly used in mathematics and bear them in mind firmly,and be well versed in the definitions,formulas as well as the technical terms in the field of mathematics.In order that he may be able to build up the foundation of the mathematical subject and master it well for pursuing advanced study.
为了打好数学基础,掌握好数学,以便学习深造,一个学数学的人必须熟悉和牢记数学中常用的记号和符号,精熟定义、公式以及术语。
[例2]The method normally employed for free electrons to be produced in electron tubes is thermic emission,in which advantage is taken of the fact that,if a solid body is heated sufficiently,some of the electrons that it contains will escape from its surface into the surrounding space.
当固体加热到足够温度时,它所含的电子就会有一部分离开固体表面而飞到周围的空间中去;这种现象称为热离子放射。通常,电子管就利用这种现象产生自由电子。
[例3]Iron rusts at its exposure to the open air on account of the corrosion made by the destructive chemical attack of a metal coming into contact with such media as air,water and moisture.
金属在接触空气、水和湿气等介质时会受到破坏性的化学侵蚀,由于这种腐蚀,铁暴露在露天时会生锈。
(3)分句译法。当英语长句各个成分在意义上不紧密时,可把长句中的短语或从句分别译成独立的句子,有时为了连贯,可加适当的词语。
[例1]On account of the accuracy and ease with which resistance measurements may be made and well-known manner in which resistance varies with temperature,it is common to use this variation to indicate changes in temperature.
我们都知道,电阻的大小是随温度变化而变化的,用电阻进行测量既精确,又方便,因此通常都用电阻的变化来表示温度的变化。
[例2]The law of universal gravitation states that every particle of matter in the universe attracts every other with a force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
万有引力定律表示:宇宙中每种物质的粒子都以一种力量吸引其他物质的粒子,这种力量与物质粒子的质量成正比,与它们之间距离的平方成反比。
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。




