前面已经给出了沙尘起沙通量和沙尘浓度水平分布的模拟结果,这里将给出对沙尘和污染物质随时间变化以及对垂直空间结构模拟结果的验证与分析。图58-6给出了模拟的沙尘浓度与观测的TSP浓度在北京随时间的变化。由图可见,模拟结果与观测吻合得较好。3月20日中午的最高沙尘浓度峰值,其出现的时间和浓度大小,都被模拟得很好,21和22日晚的2个小的峰值模式也捕捉到了,只是在出现的时间上有些偏差。3月20日晚上的次峰值,在模拟结果中没有体现出来。其中一个原因是下午模拟的浓度偏高,掩盖了晚上的次峰;另外一个原因是,晚上浓度高峰期间的沙尘,主要来自北京西北方向的沙漠及其周边农田,由于模式中农田的起沙排放因子比较低,这部分的起沙量相对偏低,从而造成模拟的偏差。总体而言,模式较好地模拟出了沙尘到达北京的时间,以及在此期间的变化。沙尘于21日到达上海,由PM 10观测值可以看出,颗粒物浓度有2个邻近的峰值。模式成功地模拟出了这2个峰值,只是在出现的时间上有些偏差,且第二个峰值的浓度,比实际的PM 10浓度偏低。模式可以很好地模拟出这次沙尘暴期间颗粒物的时间变化。

图58-6 模拟地面沙尘浓度和观测TSP浓度的对比(彩图见下载文件包,网址见14页脚注)
(a)2002年3月19—22日观测到的TSP与模式模拟结果对比(模式结果选用与观测相对应的时间平均值,下同);(b)2002年3月18—22日上海PM 10观测值与模式结果对比。
图58-7为模拟沙尘和硫酸盐(二次反应生成)的浓度,以及观测的沙尘气溶胶消光系数在北京的时间-高度剖面图。由图可见,沙尘首先从高层到达北京,浓度高值在3月19日夜间出现于500~1 000 m的高度层上,随后逐渐沉降到低层。20日早上当地时间10:00左右,更高浓度的沙尘气团沿地面到达北京,模拟的沙尘浓度与消光系数的观测结果吻合较好,说明模式可以很好地模拟出沙尘在北京的垂直结构变化。从SO 24-浓度的变化,可以看出沙尘到来之前SO 24-的浓度较高;在沙尘暴主体到达之后,由于风速迅速增大,SO 24-的浓度随之下降,沙尘与硫酸盐的混合,大多发生在高层沙尘的沉降期。
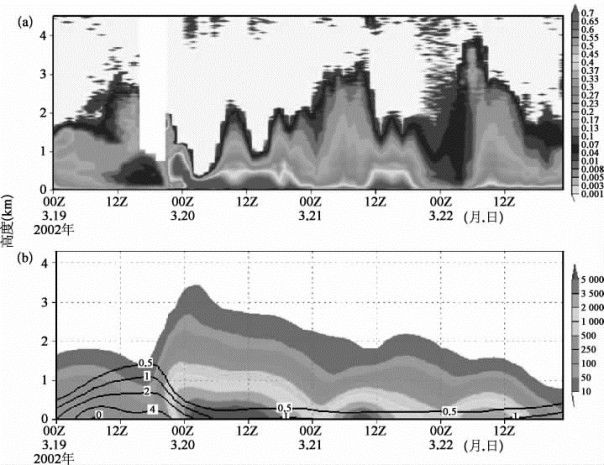
图58-7 北京T-H剖面图[1](彩图见图版第42页,也见下载文件包,网址见正文14页脚注)
(a)雷达观测的沙尘气溶胶消光系数(km-1);(b)模拟的沙尘(阴影)和硫酸盐浓度(等值线)。
参考文献
[1] 方宗义,王炜.2002年中国沙尘暴的若干特征分析.应用气象学报,2003,14(5):513-521.
[2] 牛若云,薛建军.2002年春季我国沙尘天气特征及成因分析.气象,2003,29(7):43-48.
[3] 庄国顺,郭敬华,袁惠,等.2000年中国沙尘暴的组成、来源、粒径分布及其对全球环境的影响.科学通报,2001,46(3):191-197.
[4] Yuan H,Wang Y,Zhuang G S.The simultaneous determination of organic acid,MSA with inorganic anions in aerosol and rain-water by ion chromatography.Journal of Instrumental Analysis(in Chinese),2003,6:12-16.
[5] Sugimoto N,Uno I,Nishikawa M,et al.Record heavy Asian dust in Beijing in 2002:Observations and model analysis of recent events.Geophysical Research Letters,2004,30(12):1640.doi:10.1029/2002GL016349.
[6] Taylor S R,Mclennan S M.The continental crust:Its composition and evolution.Oxford,England:Blackwells,1985.
[7] Zhang X Y,Gong S L,Shen Z X,et al.Characterization of soil dust aerosol in China and its transport and distribution during 2001 ACE-Asia:1.Network observations.Journal of Geophysical Research,2003,108(D9):4261.doi:10.1029/2002JD002632.
[8] Hueglin C,Cehrig R,Baltensperger U,et al.Chemical characteristics of PM2.5,PM 10 and coarse particles at urban,near-city and rural sites in Switzerland.Atmospheric Environment.2005,39,637-651.
[9] Zhang R,Arimoto R,An J,et al.Ground observation of a strong dust storm in Beijing in March 2002.Journal of Geophysical Research,2005,110(D18S06):doi:10.1029/2004JD004589.
[10] Han Z,Ueda H,Matsuda K,et al.Model study on particle size segregation and deposition during Asian dust events in March 2002.Journal of Geophysical Research,2004,109(D19205):doi:10.1029/2004JD004920.(https://www.xing528.com)
[11] Park S,In H.Parameterization of dust emission for the simulation of the yellow sand(Asian dust)event observed in March 2002 in Korea.Journal of Geophysical Research,2003,108(D19):4618.doi:10.1029/2003JD003484.
[12] Shao Y,Yang Y,Wang J,et al.Northeast Asian dust storms:Real-time numerical prediction and validation.Journal of Geophysical Research,2003,108(D22):4691.doi:10.1029/2003JD003667.
[13] Draxler R R,Hess G D.An overview of the Hysplit-4 modeling system for trajectories,dispersion,and deposition.Australian Meteorological Magazine,1998,47:295-308.
[14] 张小曳,张光宇,朱光华,张德二,等.中国源区粉尘的元素示踪.中国科学(D辑),1996,26(5):423-430.
[15] 郑春江.中华人民共和国土壤环境背景值图集.北京:中国环境科学出版社,1994.
[16] 韩力慧,庄国顺,孙业乐,等.北京大气颗粒物污染本地源与外来源的区分——元素比值Mg/Al示踪法估算矿物气溶胶外来源的贡献.中国科学(B辑),2005,35(3):237-246.
[17] Nishikawa M,Kanamori S,Nobuko K,et al.Kosa aerosol as eolian carrier of anthropogenic material.The Science of the Total Environment,1991,107:13-27.
[18] Borbély-Kiss I,Koltay E,SzabóG Y,et al.Composition and sources of urban and rural atmospheric aerosol in eastern Hungary.Journal of Aerosol Science,1998,30(3):369-391.
[19] Hien P D,Binh N T,Truong Y,et al.Comparative receptor modeling study of TSP,PM 2 and PM 2-10 in Ho Chi Minh City.Atmospheric Environment,2001,35:2699-2678.
[20] Morawska L,Zhang J.Combustion sources of particles.1.Health relevance and source signatures.Chemosphere,2002,49:1045-1058.
[21] Jordan C E,Dibb J E,Anderson B E,et al.Uptake of nitrate and sulfate on dust aerosols during TRACE-P.Journal of Geophysical Research,2003,108(D21):8817.doi:10.1029/2002JD003101.
[22] Hu M,He L,Zhang Y,et al.Seasonal variation of ionic species in fine particles at Qingdao,China.Atmospheric Environment,2002,36:5853-5859.
[23] 王自发,黄美元,高会旺,等.关于中国和东亚酸性物质的输送研究Ⅱ.硫化物浓度空间分布特征及季节变化.大气科学,22(5):694-700.
[24] 中国科学院兰州沙漠所北京风沙课题组.北京地区风沙活动及其整治的初步研究.中国沙漠,1987,7(3):1-15.
[25] Zhang D,Iwasaka Y.Nitrate and sulphate in individual Asian dust-storm particles in Beijing,China in spring of 1995 and 1996.Atmospheric Environment,1999,33:3213-3223.
[26] Wang Y,Zhuang G,Sun Y,et al.Water-soluble part of the aerosol in the dust storm season—Evidence of the mixing between mineral and pollution aerosols.Atmospheric Environment,2005,39:7020-7029.
【注释】
[1]图中Z是绘图用的软件里面自带的时间标识,表示世界时。如12Z表示世界时12:00。00Z表示世界时00:00。
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。




