自从2013年元月中国东部发生了一场有史以来持续时间最长的严重雾霾至今,霾污染每年都光顾中国中东部的大多数城市。一般而论,大气中的污染物和适当的气象条件是产生雾霾的决定性因素。工业污染和交通污染(主要是机动车排放的污染物)是人为污染的2类主要来源。燃煤排放的SO2以及由其进一步氧化所形成的硫酸盐气溶胶,是工业污染产生雾霾的主要成因。近10年来,中国汽车数量呈指数上升的发展态势,其排放的污染物也急剧增加(图46-6所示),已成为触发雾霾产生的另一个主要原因。在前几章的论述中已经指出,导致能见度减少和发生雾霾的大气污染物,主要有以下4类组分:有机气溶胶、硫酸盐、硝酸盐、黑碳。机动车排放的有机烃,是有机气溶胶的主要来源;机动车排放的氮氧化物,是硝酸盐的主要来源;机动车所使用的柴油或汽油的未完全燃烧所产生而排放的颗粒物,又是大气中黑碳的主要来源。由此可见,在导致能见度降低并进而产生雾霾的4类主要组分中,其中3类直接与机动车排放到大气中的污染物有关。在过去的10多年间,中国包括京津冀地区、长三角地区中东部广大地区的大气污染状况,总体上呈上升态势,甚至于自从2013年以来,大范围地同时发生雾霾。考察人为污染物的2类主要来源之一的燃煤,在过去10多年来,中国各地燃煤总量有所下降,加之燃煤脱硫取得了十分显著的成效,SO 2排放总量略有下降。基于各地的监测数据,各地大气中的SO2以及因之形成的硫酸盐浓度有减无增。这一结果表明,在过去的10多年,燃煤对产生雾霾天气的贡献并无增加。相对于工业污染源(主要是燃煤),交通源(主要是机动车排放)所产生的有机气溶胶、硝酸盐和黑碳等大气污染物,在过去的10多年间均是有增无减。显然,交通源对产生雾霾天气的相对贡献,在过去的10多年间是大大增加了。显而易见,在同样的气象条件下,近年来频频发生的雾霾,与机动车排放污染物的急剧增加密切相关。换句话说,交通源的排放,在某种意义上成为近年来大范围同时发生雾霾的“触发”因素。
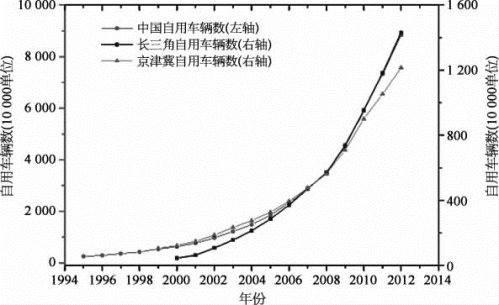
图46-6 中国机动车数量的急剧增加(彩图见图版第33页,也见下载文件包,网址见正文14页脚注)
参考文献
[1] Gelencs R A,May B,Simpson D,et al.Source apportionment of PM 2.5 organic aerosol over Europe:Primary/secondary,natural/anthropogenic,and fossil/biogenic origin.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres(1984-2012),2007,112(D23):D23S04.
[2] Heald C L,Jacob D J,Park R J,et al.Transpacific transport of Asian anthropogenic aerosols and its impact on surface air quality in the United States.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres(1984-2012),2006,111(D14):D14310.
[3] Huang K,Zhuang G,Lin Y,et al.Impact of anthropogenic emission on air quality over a megacity-revealed from an intensive atmospheric campaign during the Chinese Spring Festival.Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2012,12(23):11631-11645.
[4] Streets D G,Yan F,Chin M,et al.Anthropogenic and natural contributions to regional trends in aerosol optical depth,1980-2006.Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2009,114(D01):D011624.
[5] Cheng Z,Wang S,Fu X,et al.Impact of biomass burning on haze pollution in the Yangtze River Delta,China:A case study in summer 2011.Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2014,14(9):4573-4585.
[6] Lang J,Cheng S,Wei W,et al.A study on the trends of vehicular emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei(BTH)region,China.Atmospheric Environment,2012,62:605-614.
[7] Wang J,Ho SS H,Ma S,et al.Characterization of PM2.5 in Guangzhou,China:Uses of organic markers for supporting source apportionment.Science of the Total Environment,2016,550:961-971.
[8] Wang F,Lin T,Feng J,et al.Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM 2.5 using positive matrix factorization modeling in Shanghai,China.Environmental Science:Processes&Impacts,2015,17(1):197-205.
[9] Zheng M,Yan C,Wang S,et al.Understanding PM 2.5 sources in China:Challenges and perspectives.National Science Review,2017,4(6):801-803.
[10] 中华人民共和国环境保护部.中国机动车管理年报,2017.
[11] Sun Y L,Jiang Q,Wang Z F,et al.Investigation of the sources and evolution processes of severe haze pollution in Beijing in January 2013.Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres,2014,119(7):4380-4398.
[12] Huang K,Zhuang G,Lin Y,et al.Impact of anthropogenic emission on air quality over a megacity—Revealed from an intensive atmospheric campaign during the Chinese Spring Festival.Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2012,12(23):11631-11645.
[13] Deng J,Zhang Y,Hong Y,et al.Optical properties of PM 2.5 and the impacts of chemical compositions in the coastal city Xiamen in China.Science of the Total Environment,2016,557-558:665-675.
[14] 徐昶,沈建东,何曦,等.杭州无车日大气细颗粒物化学组成形成机制及光学特性.中国环境科学,2013(3):392-401.
[15] Arimoto R,Duce R A,Savoie D L,et al.Relationships among aerosol constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West A.Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres,1996,101(D1):2011-2023.
[16] Yao X,Chan C K,Fang M,et al.The water-soluble ionic composition of PM 2.5 in Shanghai and Beijing,China.Atmospheric Environment,2002,36(26):4223-4234.
[17] Duan L,Xiu G,Feng L,et al.The mercury species and their association with carbonaceous compositions,bromine and iodine in PM2.5 in Shanghai.Chemosphere,2016,146:263-271.
[18] Wang Y,Zhuang G S,Zhang X Y,et al.The ion chemistry,seasonal cycle,and sources of PM 2.5 and TSP aerosol in Shanghai.Atmospheric Environment,2006,40(16):2935-2952.
[19] Yu X,Ma J,An J,et al.Impacts of meteorological condition and aerosol chemical compositions on visibility impairment in Nanjing,China.Journal of Cleaner Production,2016,112-120.
[20] Ye B M,Ji X L,Yang H Z,et al.Concentration and chemical composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai for a 1-year period.Atmospheric Environment,2003,37(4):499-510.
[21] Yang H,Yu J Z,Ho S S H,et al.The chemical composition of inorganic and carbonaceous materials in PM 2.5 in Nanjing,China.Atmospheric Environment,2005,39(20):3735-3749.
[22] 陈魁,银燕,魏玉香,等.南京大气PM_(2.5)中碳组分观测分析.中国环境科学,2010,30(8):1015-1020.(https://www.xing528.com)
[23] Dan M,Zhuang G S,Li X X,et al.The characteristics of carbonaceous species and their sources in PM 2.5 in Beijing.Atmospheric Environment,2004,38(21):3443-3452.
[24] Cao G,Zhang X,Zheng F.Inventory of black carbon and organic carbon emissions from China.Atmospheric Environment,2006,40(34):6516-6527.
[25] Feng J,Chan C K,Fang M,et al.Characteristics of organic matter in PM 2.5 in Shanghai.Chemosphere,2006,64(8):1393-1400.
[26] Turpin B J,Huntzicker J J.Secondary formation of organic aerosol in the Los Angeles basin:A descriptive analysis of organic and elemental carbon concentrations.Atmospheric Environment Part A General Topics,1991,25(2):207-215.
[27] Strader R,Lurmann F,Pandis S N.Evaluation of secondary organic aerosol formation in winter.Atmospheric Environment,1999,33(29):4849-4863.
[28] Turpin B J,Huntzicker J J.Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS.Atmospheric Environment,1995,29(23):3527-3544.
[29] Castro L M,Pio C A,Harrison R M,et al.Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres:Estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations.Atmospheric Environment,1999,33(17):2771-2781.
[30] 姚婷婷,黄晓锋,何凌燕,等.深圳市冬季大气消光性质与细粒子化学组成的高时间分辨率观测和统计关系研究.中国科学:化学,2010(8):206-214.
[31] Chan Y C,Simpson R W,Mctainsh G H,et al.Source apportionment of visibility degradation problems in Brisbane(Australia)using the multiple linear regression techniques.Atmospheric Environment,1999,33(19):3237-3250.
[32] Sisler J F,Malm W C.Interpretation of trends of PM 2.5 and reconstructed visibility from the IMPROVE network.Air Repair,2000,50(5):775-789.
[33] 徐昶,沈建东,叶辉,等.杭州黑碳气溶胶污染特性及来源研究.中国环境科学,2014(12):3026-3033.
[34] 边海,韩素芹,张裕芬,等.天津市大气能见度与颗粒物污染的关系.中国环境科学,2012,32(3):406-410.
[35] Cao JJ,Wang Q Y,Chow J C,et al.Impacts of aerosol compositions on visibility impairment in Xi'an,China.Atmospheric Environment,2012,59:559-566.
[36] Liu G,Li J,Wu D,et al.Chemical composition and source apportionment of the ambient PM 2.5 in Hangzhou,China.Particuology,2015,18:135-143.
[37] 包贞,冯银厂,焦荔,等.杭州市大气PM2.5和PM 10污染特征及来源解析.中国环境监测,2010(2):44-48.
[38] 王书肖.长三角区域霾污染特征、来源及调控策略.科学出版社,2016.
[39] Wang Y,Zhuang G,Zhang X,et al.The ion chemistry,seasonal cycle,and sources of PM 2.5 and TSP aerosol in Shanghai.Atmospheric Environment,2006,40(16):2935-2952.
[40] Fu Q,Zhuang G,Wang J,et al.Mechanism of formation of the heaviest pollution episode ever recorded in the Yangtze River Delta,China.Atmospheric Environment,2008,42(9):2023-2036.
[41] Huang K,Zhuang G S,Lin Y F,et al.How to improve the air quality over megacities in China:Pollution characterization and source analysis in Shanghai before,during,and after the 2010 World Expo.Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2013,13(12):5927-5942.
[42] Wang Q,Zhuang G,Huang K,et al.Probing the severe haze pollution in three typical regions of China:Characteristics,sources and regional impacts.Atmospheric Environment,2015,120:76-88.
[43] 王荟,王格慧,高士祥,等.南京市大气颗粒物春季污染的特征.中国环境科学,2003(1):56-60.
[44] Wang H,An J,Cheng M,et al.One year online measurements of water-soluble ions at the industrially polluted town of Nanjing,China:Sources,seasonal and diurnal variations.Chemosphere,2016,148:526-536.
[45] Wang Y,Zhuang G S,Tang A H,et al.The ion chemistry and the source of PM2.5 aerosol in Beijing.Atmospheric Environment,2005,39(21):3771-3784.
[46] Wang Q Z,Zhuang G S,Huang K,et al.Probing the severe haze pollution in three typical regions of China:Characteristics,sources and regional impacts.Atmospheric Environment,2015,120:76-88.
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。




