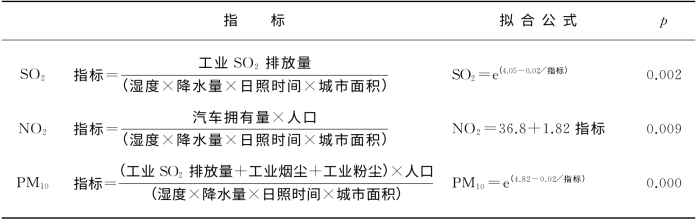
中国城市的大气污染分布,是各城市的局地排放源与气象条件等因素综合作用的结果。基于各城市湿度和降雨量等气象条件、人口、面积和工业废物排放量等年均统计数据(来自1999年《国家统计年鉴》),采用简单的影响因子,分别拟合大气污染物PM 10、SO2和NO2在不同城市的浓度。大气污染物的影响因子以及拟合公式的计算结果见表21-3。①SO2的影响因子为:指标(index)=工业SO 2排放量/(湿度×降水量×日照时间×城市面积)。SO2的浓度与其影响因子成S形曲线关系,拟合公式为SO 2=e(4.05-0.02/指标)[1],其p=0.002<0.01。(p<0.01意味着在α=0.01检验水平上);②NO 2的影响因子为:指标=汽车拥有量×人口/(湿度×降水量×日照时间×城市面积)。NO 2的浓度与其影响因子成直线关系,拟合公式为:NO2=36.8+1.82指标,其p=0.009<0.01。③PM 10的影响因子为:指标=(工业SO2排放量+工业烟尘+工业粉尘)×人口/(湿度×降水量×日照时间×城市面积)。PM 10的浓度与其影响因子成S形曲线关系,拟合公式为SO2=e(4.82-0.02/指标),其p=0.000<0.01。这里,工业SO 2排放量、工业烟尘和工业粉尘等,代表工业废物排放量,显示该城市的工业化程度;汽车拥有量代表机动车尾气排放量;人口代表居民采暖和烹饪等生活污染物排放量。可见,它们与SO 2、NO 2和PM 10浓度呈显著的正相关。而湿度和日照时间代表这些一次污染物转化为二次污染物的多少,降雨量作为该地区污染气溶胶的稀释因素,它们与SO 2、NO 2和PM 10浓度呈显著的负相关。拟合公式的p值均小于0.01,可见,这些影响因子与实际污染物的浓度值符合得很好,正说明了局地排放源和气候条件等多种因素的综合作用,决定了中国城市大气污染的区域性分布。
表21-3 大气污染物的影响因子以及拟合公式
参考文献
[1] Zhang R J,Wang M X,Pu Y F,et al.Analysis on the chemical and physical properties of“2000.4.6”super dust storm in Beijing.Climatic and Environmental Research,2000,5:259-266.
[2] Sun Y,Zhuang G,Yuan H,et al.Characteristics and sources of 2002 super dust storm in Beijing.Chinese Science Bulletin,2004,49(7):698-705.
[3] Guo J,Rahn K A,Zhuang G,et al.A mechanism for the increase of pollution elements in dust storms in Beijing.Atmospheric Environment,2004,38(6):855-862.
[4] Zhuang G S,Guo J H,Yuan H,et al.Coupling and feedback between iron and sulphur in air-sea exchange.Chinese Science Bulletin,2003,48:1080-1086.
[5] Liu T S,Gu X F,An Z S,et al.The dust fall in Beijing,China on April 18,1980.Geological Society of America Special Paper,1981,186:149-157.
[6] Lin T H.Long-range transport of yellow sand to Taiwan in Spring 2000:Observed evidence and simulation.Atmospheric Environment,2001,35:5873-5882.
[7] Murayama T,Sugimoto N,Uno I,et al.Ground-based network observation of Asian dust events of April 1998 in East Asia.Journal of Geophysical Research,2001,106:18345-18359.
[8] Yi S M,Lee E Y,Holsen T M.Dry deposition fluxes and size distributions of heavy metals in Seoul,Korea during yellow-sand events.Aerosol Science and Technology,2001,35:569-576.
[9] Chun Y,Kim J,Choi J C,et al.Characteristic number size distribution of aerosol during Asian dust period in Korea.Atmospheric Environment,2001,35:2715-2721.
[10] Uematsu M,Yoshikawa A,Muraki H,et al.Transport of mineral and anthropogenic aerosols during a Kosa even over East Asia.Journal of Geophysical Research,2002,107(D7):4059.
[11] Ma C J,Kasahara M,Holler R,et al.Characteristics of single particles sampled in Japan during the Asian dust storm period.Atmospheric Environment,2001,35(15):2707-2714.
[12] Husar R B,Tratt D M,Schichtel B A,et al.The Asian dust events of April 1998.Journal of Geophysical Research,2001,106:18317-18330.
[13] Perry K D,Cahill T A,Schnell R C,et al.Long-range transport of anthropogenic aerosols to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration baseline station at Mauna Loa Observatory,Hawaii.Journal of Geophysical Research,1999,104:18521-18533.
[14] Tratt D M,Frouin R J,Westphal D L.April 1998 Asian dust event:A southern California perspective.Journal of Geophysical Research,2001,106:18371-18379.
[15] Zhuang G,Huang R H,Wang M X,et al.Great progress in study on aerosol and its impact on the global environment.Progress in Natural Science,2002,12(6):407-413.
[16] Zhang D,Iwasaka Y.Nitrate and sulfate in individual Asian dust-storm particles in Beijing,China in spring of 1995 and 1996.Atmospheric Environment,1999,33(19):3213-3223.
[17] He K B,Yang F,Ma Y L,et al.The characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing,China.Atmospheric Environment,2001,35(29):4959-4970.
[18] Yuan H,Wang Y,Zhuang G.MSA in Beijing aerosol.Chinese Science Bulletin,2004,49(10):1020-1025.
[19] Ye B,Ji X,Yang H,et al.Concentration and chemical composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai for a 1 yr period.Atmospheric Environment,2003,37:499-510.
[20] Yao X,Chan C K,Fang M,et al.The water-soluble ionic composition of PM 2.5 in Shanghai and Beijing,China.Atmospheric Environment,2002,36:4223-4234.(https://www.xing528.com)
[21] Cheng Z L,Lam K S,Chan L Y,et al.Chemical characteristics of aerosols at coastal station in Hong Kong.I.Seasonal variation of major ions,halogens and mineral dusts between 1995 and 1996.Atmospheric Environment,2000,34(17):2771-2783.
[22] Ho K F,Lee S C,Chan C K,et al.Characterization of chemical species in PM2.5 and PM10 aerosols in Hong Kong.Atmospheric Environment,2003,37(1):31-39.
[23] Lee E,Chan C K,Paatero P,et al.Application of Positive Matrix factorization in source apportionment of particulate pollutants in Hong Kong.Atmospheric Environment,1999,33:3201-3212.
[24] 苏福庆,高庆先,张志刚,等.北京边界层外来污染物输送通道.环境科学研究,2004,17(1):25-29,40.
[25] 任阵海,高庆先,苏福庆,等.北京大气环境的区域特征与沙尘影响.中国工程科学,2003,15(2):49-56.
[26] 任阵海,万本太,苏福庆,等.当前中国大气环境质量的几个特征.环境科学研究,2004,17(1):1-5.
[27] Wang Y,Zhuang G S,Tang A,et al.The ion chemistry and the source of PM 2.5 aerosol in Beijing.Atmospheric Environment,2005,39(21):3771-3784.
[28] Yao X H,Lau A P,Fang M,et al.Size distributions and formation of ionic species in atmospheric particulate pollutants in Beijing,China:1-inorganic ions.Atmospheric Environment,2003,37:2991-3000.
[29] 张小曳,沈志宝,张光宇,等.青藏高原远源西风粉尘与黄土堆积.中国科学(D辑),1996,26(2):147-153.
[30] Xiao H,Liu C.Chemical characteristics of water-soluble components in TSP over Guiyang,SW China,2003.Atmospheric Environment,2004,38:6297-6306.
[31] Arimoto R,Duce R A,Savoie D L,et al.Relationships among aerosol constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during Pem-West A.Journal of Geophysical Research,1996,101:2011-2023.
[32] 籍静钰,李萍.包头市区大气颗粒物中硫酸根等四种阴离子含量水平及特征的研究.内蒙古环境保护,1997,9(4):32-35.
[33] 李连科,栗俊,高广智,等.大连海域大气气溶胶特征分析.海洋环境科学,1997(3):46-52.
[34] Hu M,He L,Zhang Y,et al.Seasonal variation of ionic species in fine particles at Qingdao,China.Atmospheric Environment,2002,36:5853-5859.
[35] Wang G,Huang L,Gao S X,et al.Characterization of water-soluble species of PM 10 and PM 2.5 aerosols in urban area in Nanjing,China.Atmospheric Environment,2002,36(8):1299-1307.
[36] Ye B,Ji X,Yang H,et al.Concentration and chemical composition of PM 2.5 in Shanghai for a 1 yr period.Atmospheric Environment,2003,37:499-510.
[37] 吴兑,陈位超.广州气溶胶质量谱的年变化特征.气象学报,1994,52(4):499-533.
[38] 高金和,王玮,杜渐,等.厦门春季气溶胶特征初探.环境科学研究,1996,9(5):33-37.
[39] Fang G C,Chang C N,Wu Y S,et al.Characterization of chemical species in PM 2.5 and PM 10 aerosols in suburban and rural sites of central Taiwan.The Science of the Total Environment,1999,234:203-212.
[40] Ho K F,Lee S C,Chan C K,et al.Characterization of chemical species in PM2.5 and PM 10 aerosols in Hong Kong.Atmospheric Environment,2003,37(1):31-39.
[41] 万小芳,吴增茂,常志清,等.南黄海和东海海域营养盐等物质大气入海通量的再分析.海洋环境化学,2002,21(13):14-18.
【注释】
[1]这里e为自然对数的底数2.718 28。
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。




