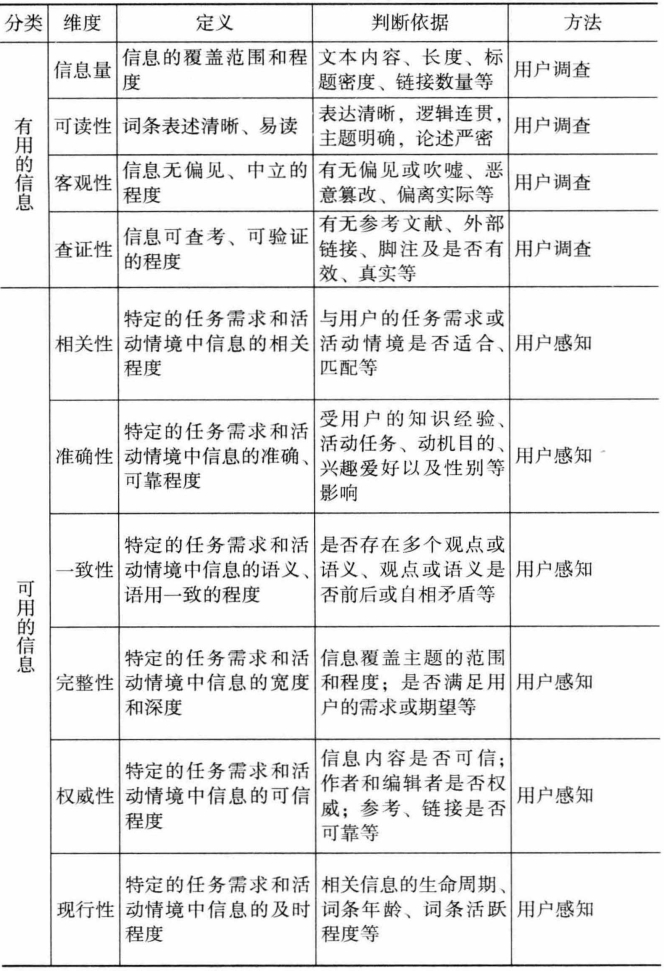
目前国内外理论界和实践界对信息质量属于多维的概念已形成普遍共识。在信息质量研究领域,麻省理工学院的Wang教授是国际著名的代表人物和先驱,他继1996年提出内在信息质量、情景信息质量、表象信息质量和可访问性信息质量之后[78],又于2002年进一步提出合理的信息、可靠的信息、有用的信息和可用的信息等对信息质量进行分类[79]。Arazy认为维基百科词条是开放存取的,任何用户都可以对它们自由、方便地进行访问,因此,不存在可访问性信息质量问题,所以,他在对维基百科词条信息质量维度进行评分一致性研究时只选取了内在信息质量、情景信息质量、表象信息质量三种类型的信息质量维度。Stvili则基于对信息活动方式等的理论分析提出从内在信息质量、情境信息质量、权威信息质量对信息质量维度进行分类[80]。由于维基百科词条仍是一种特殊情境的Web信息,Yaari也证实当参与者对维基百科词条进行评估时仍然使用一般的Web信息评估属性[81]。Knight和Burn研究得出了最近十年Web信息质量评价框架和模型中最常用的准确性、一致性、完整性等一般的信息质量维度[82],因此,本书认为应将它们融入维基百科词条的信息质量启发式评价框架之中。详尽可能性模型(Elaboration Likelihood Model,ELM)理论认为当用户被驱动或具有主题相关的知识时会选择使用“核心路线”,而当知识和激励缺少时会选择“次要路线”,并根据外在特征做出决定[83]。Adelson曾证明初学者在对信息质量进行判断时由于缺乏主题相关的领域知识只能借助写作风格、参考信息等形式特征对信息进行判断[84]。除此之外,用户对信息质量的感知和判断还与用户的使用动机和使用目的有关,如是为生产知识还是了解信息,是获取事实性信息、背景性信息还是参考性信息等。综上,本书从信息价值的视角出发,基于以上理论基础构建出一套符合ELM理论的、层次递进的、包含合理的信息、有用的信息、可用的信息的维基百科词条信息质量启发式评价框架,这是一个包含概念、关系、分类和方法学的多维结构,能够为维基百科词条的信息质量评价提供相应基准、标准或参考,并适合不同类型的信息用户在不同情境下使用(如初学者或主题不熟悉用户主要基于合理和有用的信息视角对维基百科词条进行识别和判断;领域专家或知识生产者主要基于可用的信息视角对维基百科词条进行识别和判断等)。详见表6-19。
表6-19 维基百科词条信息质量启发式评价框架

续表
【注释】
[1]岳剑波.信息管理基础[M].北京:清华大学出版社,1999:67.
[2]Wand Y,Wang R Y.Anchoring Data Quality Dimensions in Ontological Foundations[J].Communications of the ACM,1996,39(11):86-95.
[3]Wang R Y.A Product Perspective on Total Data Quality Management[J].Communications of the ACM,1998,41(2):58-65.
[4]Lee Y W,Strong D W,Kahn B K,et al.AIMQ:A Methodology for Information Quality Assessment[J].Information & Management,2002,40(2):133-146.
[5]Stvilia B,Gasser L.A Framework for Information Quality Assessment[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2007,58(12):1720-1733.
[6]Kuhlthau C C.A Principle of Uncertainty for Information Seeking[J].Journal of Documentation,1993(49):339-355.
[7]Wilson P.Situational Relevance[J].Information Storage and Retrieval,1973(9):457-469.
[8]Harter P.Psychological Relevance and Information Science[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science,1992,43(9):602-615.
[9]成颖.信息检索相关性判据及应用研究[M].北京:科学出版社,2011:13.
[10]Wang R Y.A Product Perspective on Total Data Quality Management[J].Communications of the ACM,1998,41(2):58-65.
[11]Wang P,Soergel D.A Cognitive Model of Document Use During a Rese arch Project.Study I:Document Selection[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science,1998,49(2):115-133.
[12]Rieh S Y.Judgment of Information Quality and Cognitive Authority in the Web[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2002,53(2):145-161.
[13]Greisdorf H.Relevance Thresholds:A Multistage Predictive Model of How Users Evaluate Information[J].Information Processing and Management,2003,39(3):403-423.
[14]Tombros A,Ruthven I,Jose J M.How Users Assess Web Pages for Information Seeking[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2005,56(4):327-344.
[15]Savolainen R,Kari J.User-defined Relevance Criteria in Web Searching[J].Journal of Documentation,2006,62(6):685-707.
[16]Fink-Shamit N,Bar-Ilan J.Information Quality Assessment on the Web—An Expression of behavior[EB/OL].[2012-12-01].http://www.information r.net/ir/13-4/paper357.html.
[17]胡磊.互联网学术信息可信性评价判据研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2012,48(5):712-718.
[18]刘冰,张耀辉.基于网络用户体验和感知的信息质量影响因素模型实证研究[J].情报学报,2013,32(6):663-672.
[19]刘冰,卢爽.基于用户体验的信息质量综合评价体系研究[J].图书情报工作,2011,55(22):56-59.
[20]Xiel,Benoit Ⅲ E.Search Result List Evaluation Versus Document Evaluation Similar ities and Differences[J].Journal of Documentation,2013,69(1):49-80.
[21]Knight S,Burn J.Developing a Framework for Assessing Information Quality on the World Wide Web[J].Informing Science,2005(8):159-172.
[22]Rieh SY.Judgment of Information Quality and Cognitive Authority in the Web[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2002,53(2):145-161.
[23]Brandgruwel S,Woper eis I,Vermetten Y.Information Problemsolving by Experts and Novices:Analysis of a Complex Cognitive Skill[J].Computers in Human Behavior,2005,21(3):487-508.
[24]Petty R E,Cacioppo J T.The Elaboration Likelihood Model of Persuasion[J].Advances in Experimental Social Psychology,1986(19):123-205.
[25]Walthen C N,Burkell J.Believe It or Not:Factors Influencing Credibility on the Web[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2002,53(2):134-144.
[26]Petty R E,Cacioppo J T.The Elaboration Likelihood Model of Per suasion[J].Advances in Experimental Social Psychology,1986(19):123-205.
[27]Lucassen T,Schraagen J M.Factual Accuracy and Trust in Information:The Role of Expertise[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2011,62(7):1232-1242.
[28]Fink-Shamit N,Bar-Ilan J.Information Quality Assessment on the Web—an Expression of behavior[EB/OL].[2012-12-01].http://www.informationr.net/ir/13-4/paper357.html.
[29]过仕明.PageRank的技术分析及网页重要性的综合评价模型[J].图书馆论坛,2006(1):80-81.
[30]Stoker D,Cooke A.Evaluation of Networked Information Sources[EB/OL].[2013-12-01].http://users.aber.ac.uk/das/texts/eval.htm.
[31]陈雅,郑建明.网站评价指标体系研究[J].中国图书馆学报,2002(5):57-60.
[32]Walthen C N,Burkell J.Believe it or not:Factors Influencing Credibility on the Web[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2002,53(2):134-144.
[33]Robins D,Holmes J,Stansbury M.Consumer Health Information on the Web:The Relationship of Visual Design and Perceptions of Credibility[J].Journal o f the American Society f o r Information Science and Technology,2010,61(1):13-29.
[34]胡磊.互联网学术信息可信性评价影响因素实证研究[J].情报理论与实践,2013,36(9):72-77.
[35]Rieh S Y.Judgment of Information Quality and Cognitive Authority in the Web[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2002,53(2):145-161.
[36]网站 声 明[EB/OL].[2012-10-05].http://www.people.com.cn/n/2013/1227/c373005-23961344.html.
[37]Harris R.Evaluating Internet Research Sources[EB/OL].[2013-12-01].http://www.mu.edu/facdev/programs/handouts/evaluate.htm.
[38]Wikipedia:Featured articles[EB/OL].[2012-10-09].https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Featured_articles.
[39]访谈进 行 中:《科研 评价指标功 与过》[EB/OL].[2015-07-09].http://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-45-905590.html.(https://www.xing528.com)
[40]Guidelines For Using The Research Blogging Icon And Site[EB/OL].[2015-04-12].http://researchblogging.org/news/?p=53.
[41]Xie,Benoit Ⅲ E.Search Result List Evaluation Versus Document Evaluation Similarities and Dif erences[J].Journal of Documentation,2013,69(1):49-80.
[42]Rieh S Y.Judgment of Information Quality and Cognitive Authority in the Web[J].Journal of the American Society for InformationScience and Technology,2002,53(2):145-161.
[43]邹永利.学术文献的非主题特征及其意义[J].中国图书馆学报,2011,137(193):100-107.
[44]Fink-Shamit N,Bar-Ilan J.Information Quality Assessment on the Web—An Expression of Behavior[EB/OL].[2012-12-01].http://www.informationr.net/ir/13-4/paper357.html.
[45]Wang R Y.A Product Perspective on Total Data Quality Management[J].Communications of the ACM,1998,41(2):58-65.
[46]丁敬达.创新知识社区内部科学交流的特征和规律[J].情报学报,2011(10):1086-1094.
[47]Fink-Shamit N,Bar-Ilan J.Information Quality Assessment on the Web-An Expression of Behavior[J].Information Research,2008,13(4):22.
[48]张智雄,张晓林,刘建华等.网络科技信息结构化监测的思路和技术方法实现[J].中国图书馆学报,2014,40(212):4-15.
[49]Richmond B.Ten C's For Evaluating Internet Sources[EB/OL].[2014-11-01].http://www.datarecoverylabs.com/evaluating-internet-resources.html.
[50]金岳霖.形式逻辑[M].北京:人民出版社,1979:281.
[51]Savolainen R.Judging the Quality and Credibility of Information in Internet Discussion Forums[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2011,62(7):1243-1256.
[52]教育部社会科学委员会学风建设委员会.高校人文社会科学学术规范指南[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2009:2-4.
[53]Liu Z M,Huang X B.Evaluating the Credibility of Scholarly Information on the Web:A Cross Cultural Study[J].The International Information & Library Review,2005,37(2):99-106.
[54]Lewandowski D,Spree U.Ranking of Wikipedia Articles in Search Engines Revisited:Fair Ranking for Reasonable Quality?[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2011,62(1):117-132.
[55]Garvin D A.Managing Quality[M].Free Press,1988:32-45.
[56]Mebrate T.A Framework for Evaluating Academic Website's Quality From Students' Perspective[D].Netherland:Delft University of Technology,2010:1-57.
[57]Wang R Y.A Product Perspective on Total Data Quality Management[J].Communications of the ACM,1998,41(2):58-65.
[58]Greisdorf H.Relevance Thresholds:A Multi-stage Predictive Model of How Users Evaluate Information[J].Information Processing and Management,2003,39(3):403-423.
[59]Schamber L.Relevance and Information Behavior[J].Annual Review of Information Science and Technology,1994,29(3):3-48.
[60]Cooper W S.On Selecting a Measure of Retrieval Ef ectiveness,Part 2:Implementation of the Philosophy[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science,1973,24(6):413-424.
[61]Wilson P.Situational Relevance[J].Information Storage and Retrieval,1973(9):457-469.
[62]Xu Y C,Chen Z.Relevance Judgments:What Do Information Users Consider Beyond Topicality[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2006,57(7):961-973.
[63]Rieh S Y.Judgment of Information Quality and Cognitive Authority in the Web[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2002,53(2):145-161.
[64]劳凯声.人文社会科学研究的问题意识、学理意识和方法意识[J].北京师范大学学报(社会科学版),2009(1):5-15.
[65]Juran J M.On Quality By Design:The New Steps For Planning Quality Into Goods and Services[M].New York:Simon & Schuster,1992:71-79.
[66]Eppler M J.Managing Information Quality:Increasing the Value of Inform Ation in Knowledge Intensive Products and Pr ocesses[M].Berlin:Springer Verlag,2003:56-79.
[67]Eppler M J.Managing Information Quality:Increasing the Value of Inform Ation in Knowledge Intensive Products and Processes[M].Berlin:Springer Verlag,2003:56-79.
[68]Xie Ⅰ,Benoit Ⅲ E.Sea rch Result List Evaluation Versus Document Evaluation Similarities and Differences[J].Journal of Documentation,2013,69(1):49-80.
[69]Rieh S Y.Judgment of Information Quality and Cognitive Authority in the Web[J].Journal of the American Society for Infor mation Science and Technology,2002,53(2):145-161.
[70]Maron N L,Kirby S K.Cur rent Models of Digital Scholarly Communication[EB/OL].[2013-09-20].http://www.arl.org/bm~doc/current-models-report.p df.
[71]Chesney T.An Empirical Examination of Wikipedia's Credibility[EB/OL].[2013-09-15].http://journals.uic.edu/ojs/index.php/fm/article/view/1413/1331.
[72]Stvili B,Gasser L.A Framework for Information Quality Assessment[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2007,58(12):1720-1733.
[73]Garvin D A.Managing Quality[M].Free Press,1988:32-45.
[74]Lewandowski D,Spree U.Ranking of Wikipedia Articles in Search Engines Revisited:Fair Ranking for Reasonable Quality?[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2011,62(1):117-132.
[75]Strong D,Lee Y,Wang R.Data Quality in Context[J].Communications of the ACM,1997,40(5),103-110.
[76]Strauss A.Negotiations:Varieties,Contexts,Processes,and Social Order[M].San Francisco:Jossey-Bass,1978:21-34.
[77]葛某智,Markus H.信息质量研究的现状与未来研究方向[J].科技资源导刊,2009,41(1):5-16.
[78]Wang R Y,Strong D M.Beyond Accuracy:What Data Quality Means to Data Consumers[J].Journal of Management Information Systems,1996,12(4):5-33.
[79]Arazy O,Kopak R.On the Measurability of Information Quality[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2011,62(1):89-99.
[80]Stvili B,Gasser L.A Framework for Information Quality Assessment[J].Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2007,58(12):1720-1733.
[81]Yaari E,etc.Information Quality Assessment of Community-generated Content—A User Study of Wikipedia[J].Journal of Information Science,2011,37(5):487-498.
[82]Knight S,Burn J.Developing a Framework for Assessing Information Quality on the World Wide Web[J].Informing Science,2005,8:159-172.
[83]Petty R E,Cacioppo J T.The Elaboration Likelihood Model of Persuasion[J].Advances in Experimental Social Psychology,1986,19:123-205.
[84]Adelson B.When Novices Surpass Experts:The Difficulty of a Task may Increase with Expertise[J].Journal of Experimental Psychology:Learning,Memory,and Cognition,1984,10(3),483-495.
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。




